Popular Searches:foot scanner | 3D scanner | 3D Printer | Design Software |


Tel :0755-86131192 86180201
Fax :0755-86180213
E-mail: [email protected]
Website: gift0755.cn
Address: 3A05, Minzhi Chamber of Commerce Building, Minzhi Avenue, Longhua District, Shenzhen
Are you here: Home > News > Industry NewsIndustry News
The principles of foot measurement by foot scanners and their common application scenarios.
Time:2025-01-17 16:21:54Source:深圳市精易迅科技有限公司Views:2
A foot scanner is a sophisticated device based on 3D imaging technology designed to capture detailed data on foot shape and dimensions. Its working principle relies on modern optical scanning, laser technology, and digital processing algorithms, enabling the generation of high-precision 3D foot models within a short time. Foot scanners are widely applied in medicine, sports science, footwear design, and health management, providing essential technological support for improving diagnostic efficiency, optimizing product design, and enhancing individual health management.
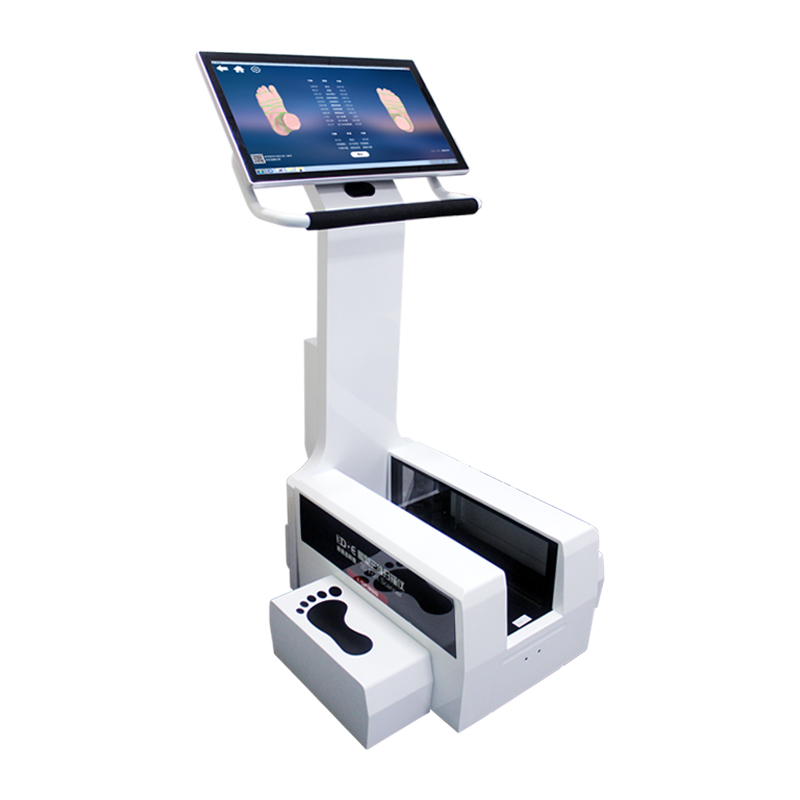
3D Foot Shape Scanner
I. Measurement Principles of Foot Scanners
1. Optical Scanning Technology
Optical scanning is one of the most commonly used technologies in foot scanners. It works by projecting a grid or stripe of light onto the surface of the foot and capturing the reflected light using cameras to create a 3D model. Based on structured light or stereo vision principles, the system calculates the displacement of light to determine the spatial coordinates of various points on the foot. This method is characterized by high precision and efficiency, enabling rapid capture of detailed foot shape features.
2. Laser Scanning Technology
Laser scanning technology uses laser beams projected onto the surface of the foot and sensors to capture the reflected laser signals. By calculating the changes in the laser path, the system generates 3D point cloud data of the foot. Laser scanning is particularly effective for complex surfaces and is well-suited for precision measurement tasks.
3. Photogrammetry Technology
Some portable foot scanners employ multi-angle photogrammetry, taking images of the foot from various angles using multiple cameras and reconstructing a 3D model with image processing algorithms. This method is cost-effective and suitable for portable and home scenarios, though its accuracy may be slightly lower than that of laser or optical scanning.
4. Integration of Pressure Sensing and Shape Analysis
Certain foot scanners combine pressure sensing technology with 3D shape analysis, capturing both the foot's 3D morphology and plantar pressure distribution. This integrated technology provides comprehensive data for dynamically assessing foot function and gait characteristics.
II. Common Application Scenarios of Foot Scanners
1. Medical Field
Diagnosis of Foot Disorders
Foot scanners play a vital role in diagnosing conditions such as flat feet, high arches, and foot pronation or supination. By capturing detailed data on foot morphology, doctors can accurately identify structural abnormalities and provide scientific support for treatment plans.Customized Orthotic Devices
Foot scanners can precisely measure patients' foot dimensions and morphology, offering accurate data for designing custom orthotic insoles and shoes. This personalized approach significantly improves correction effectiveness, reduces discomfort, and prevents further development of foot conditions.Postoperative Rehabilitation Assessment
After foot surgery, foot scanners can monitor changes in foot morphology, providing real-time data to optimize rehabilitation treatment adjustments.
2. Sports Science and Equipment Optimization
Performance Analysis
Foot scanners can capture athletes' foot characteristics and dynamic changes, offering scientific insights for optimizing performance. Designers and coaches can use scanning data to adjust footwear designs or training plans, enhancing athletes' performance and reducing injury risks.Customized Sports Footwear Design
The comfort and functionality of sports footwear are closely related to foot morphology. Using foot scanning data, footwear manufacturers can design shoes that better fit athletes’ foot shapes, improving athletic performance and comfort.
3. Footwear Design and Manufacturing
Personalized Footwear Customization
Standardized shoe sizes often fail to meet individual needs. Foot scanners capture precise foot shape data, enabling the design and manufacturing of footwear tailored to individual preferences. This customization enhances user satisfaction and drives the intelligent development of the footwear industry.Rapid Prototyping
3D models generated by foot scanners can be directly applied in footwear design and production, shortening development cycles and reducing design errors.
4. Health Management and Everyday Applications
Foot Health Monitoring
Foot morphology changes over time due to factors such as age, weight, and lifestyle. Regular scans enable users to track these changes, identify potential issues early, and take preventive measures.Home Health Devices
With the proliferation of portable scanners, consumers can easily obtain foot data to select better-fitting footwear or develop daily health plans.
Foot scanners, with their precise measurement principles and diverse application scenarios, play a crucial role in medicine, sports, design, and health management. They not only improve the efficiency and accuracy of diagnosing foot problems and designing footwear but also drive the development of personalized and intelligent technologies. As technology continues to advance, the functionalities and applications of foot scanners will expand further, contributing significantly to better foot health and enhanced quality of life.



